Introduction
Lidocaine is one of the most commonly used local anesthetics in medical procedures. It is typically applied or injected to numb specific body areas, relieving pain during surgeries, dental work, or minor medical treatments. If you’ve ever had a dental procedure or a skin biopsy, chances are you’ve experienced the numbing effects of lidocaine. But a common question among patients and those undergoing medical treatments is, How long does last?
Understanding the duration of lidocaine’s effects, its underlying mechanisms, and the factors that influence its longevity can help patients manage expectations and make informed decisions about their treatments. In this article, we will dive into how long lasts, the factors that influence its duration, its potential side effects, and other important details related to its use.
What is Lidocaine?
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic, which means it numbs specific areas of the body without affecting the entire body. It blocks nerve signals in the affected area, preventing pain sensations from reaching the brain. is often used for a variety of medical procedures, such as:
- Dental Work: To numb the gums and teeth during filling or extractions.
- Minor Surgeries: Used to numb the skin and underlying tissues before stitches or minor operations.
- Injections for Pain Relief: For nerve pain or procedures involving injections near the skin.
Lidocaine is typically applied topically, injected, or used as a patch, depending on the nature of the procedure. The purpose is to provide effective, localized pain relief without causing a loss of consciousness or major side effects.
How Long Does Lidocaine Last?
The main question many people ask when prescribed is: How long does lidocaine last? The duration of lidocaine’s effect can vary depending on several factors, including the method of administration, the dose used, and individual differences. On average lasts between 1 to 3 hours.
Duration Based on Method of Administration
The method by which lidocaine is administered plays a significant role in how long its effects last. Here’s a breakdown of how long typically lasts with different administration methods:
1. Topical Lidocaine
Topical lidocaine, which comes in creams, gels, or sprays, is usually applied to the skin or mucous membranes (such as the inside of the mouth). It numbs the surface area where it is used. The effects of topical usually last for 30 minutes to 2 hours. The duration depends on factors such as the amount used, the area of application, and the specific condition being treated.
2. Injectable Lidocaine
Injectable lidocaine is commonly used in dental procedures or minor surgeries. When injected directly into tissues, the numbing effects are typically felt within 2 to 5 minutes and can last anywhere from 1 to 3 hours. However, the effects may wear off sooner if the dose is lower or the procedure is more extensive.
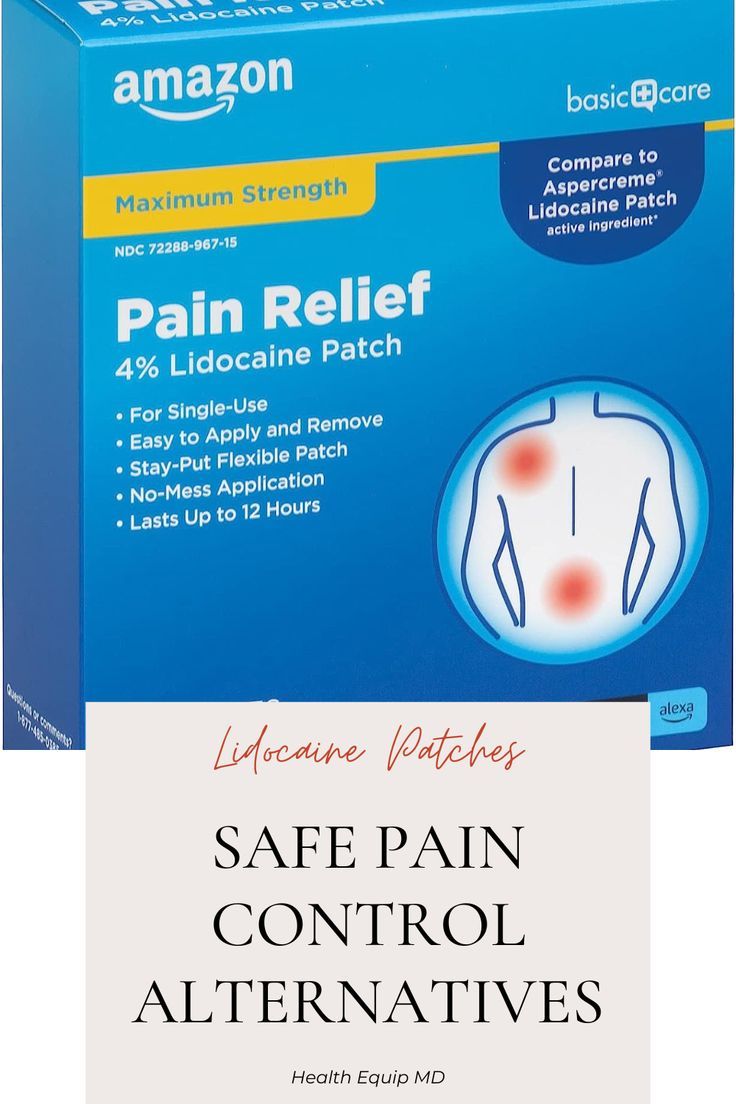
3. Lidocaine Patches
Lidocaine patches are used for managing chronic pain conditions such as post-herpetic neuralgia (nerve pain caused by shingles). These patches release slowly over some time. The effects can last 12 to 24 hours, depending on the patch type and its placement on the body.
Duration Based on Dosage
The dosage of lidocaine used will also impact how long the anesthetic effect lasts. A higher dose generally leads to a longer duration of numbing. For example, during a more invasive procedure or surgery, higher amounts of might be used to ensure that the numbing lasts long enough for the entire procedure. In such cases, the effects can last for several hours.
Factors that Affect the Duration of Lidocaine
While the average duration of lidocaine’s effects is 1 to 3 hours, several factors can influence how long it lasts. It’s important to keep these factors in mind when discussing lidocaine with a healthcare provider.
1. Blood Flow to the Area
One of the key factors that affect the duration of lidocaine is blood flow to the area where it is applied. Areas of the body with higher blood circulation, such as the face or scalp, may metabolize and eliminate more quickly. In contrast, areas with lower blood circulation, like the fingers or toes, may retain the effects of for a longer period.
2. Concentration of Lidocaine
The concentration of lidocaine used in a given procedure will impact how long its effects last. Higher concentrations can provide longer-lasting numbing. For example, a higher concentration of injectable can extend the duration of pain relief compared to a lower concentration.
3. Type of Procedure
The type of medical procedure and the tissue depth affected will influence how long lidocaine lasts. Superficial procedures like a simple skin biopsy may require less and wear off more quickly. In contrast, deeper procedures (e.g., dental extractions or joint injections) may need more and result in a longer duration of action.
4. Individual Response
Every person’s body is different, and some individuals may metabolize lidocaine more quickly than others. For example, individuals with faster metabolic rates may experience a shorter duration of action, while those with slower metabolisms may find that the effects last longer.
5. Presence of Other Medications
Certain medications, such as beta-blockers or other antiarrhythmic drugs, may interact with lidocaine and alter how the body processes the drug. These interactions can either prolong or shorten the duration of lidocaine’s effects.
Side Effects and Risks of Lidocaine
While lidocaine is generally safe when used as directed, there are potential side effects to be aware of. The side effects typically occur when the drug is used in excessive amounts or when an individual is particularly sensitive. Some common side effects of lidocaine include:
- Numbness beyond the treated area: In rare cases, lidocaine can spread to other parts of the body, causing unwanted numbness.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness may occur if the dosage is too high or the drug enters the bloodstream.
- Allergic reactions: While uncommon, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction, resulting in symptoms such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals may experience stomach discomfort after administering lidocaine.
If you experience any unusual symptoms or have concerns about side effects, it is important to contact your healthcare provider immediately.
How to Prolong the Effects of Lidocaine
In some cases, patients may want to prolong the effects of lidocaine, especially if they are undergoing a lengthy procedure or need prolonged pain relief. Some techniques to extend the effects include:
- Epinephrine Combination: Often,is combined with epinephrine (a vasoconstrictor) to reduce blood flow in the treated area. This helps to prolong the numbing effects by slowing down the body’s ability to absorb and remove the drug.
- Lidocaine Patches: For chronic pain conditions, patches can be worn for extended periods, allowing for longer-lasting pain relief.

Conclusion
In summary, the duration of lidocaine’s effects can vary, with most people experiencing relief for 1 to 3 hours. Several factors contribute to this variation, including the method of administration, dosage, and individual differences. It is essential to understand these factors to ensure you have the appropriate expectations for pain relief during and after medical procedures.
Lidocaine is a powerful tool for pain management, but it is important to use it correctly and be aware of potential side effects. By consulting with a healthcare provider, you can ensure lidocaine is used safely and effectively for your specific needs.
FAQs
1. How long does lidocaine last for dental procedures?
Lidocaine used in dental procedures typically lasts 1 to 2 hours, although this can vary depending on the method and individual factors.
2. Can the effects of lidocaine be prolonged?
Yes, lidocaine’s effects can be prolonged by combining it with epinephrine or using patches for chronic pain management.
3. Does last longer in certain parts of the body?
Yes, tends to last longer in areas with less blood flow, such as the fingers or toes and may wear off faster in areas with higher blood circulation, like the face.
4. Can I drive after receiving lidocaine?
In most cases, once the effects of lidocaine wear off, you should be able to resume normal activities. However, if you feel lightheaded or dizzy, waiting until these symptoms subside before driving is best.
5. What happens if lidocaine wears off too quickly?
If lidocaine wears off too quickly, you may experience some pain or discomfort. If this occurs during a procedure, inform your healthcare provider so they can administer more if necessary.
Explore more: hadokin