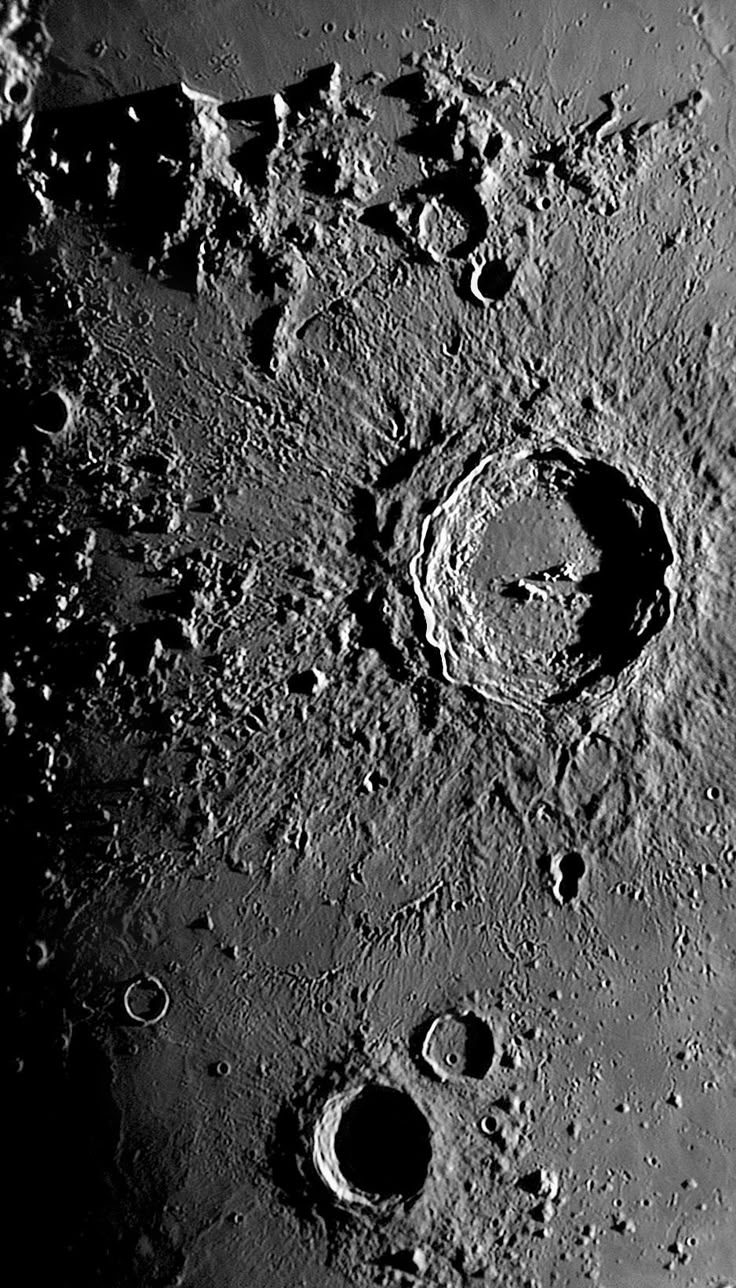
Introduction
The Moon has always been a subject of fascination for humanity. Ancient cultures saw the Moon as a celestial deity. Modern space agencies send robotic probes and astronauts to its surface. The Moon holds countless mysteries waiting to be unraveled.In recent years, lunar scans have played a crucial role in helping us understand more about this mysterious celestial body. Using cutting-edge technology, scientists have gained valuable insights into the Moon’s surface, its composition, and the possibility of future exploration and habitation.
In this article, we will explore the role of lunar in advancing our knowledge of the Moon, the major discoveries made through these scan, and what the future holds for lunar exploration.
What Are Lunar Scans?
Lunar scans refer to scanning the Moon’s surface using various sensors and imaging technologies. These scans are conducted by both robotic spacecraft and telescopes. The primary purpose of these scans is to capture detailed images and gather data about the Moon’s surface features, mineral composition, topography, and any changes or anomalies.
Lunar are used for scientific research and play a key role in planning future missions to the Moon. By understanding the surface better, space agencies can pinpoint locations for lunar bases, identify areas of interest for resource mining, and track changes in the Moon’s environment over time.
Types of Lunar Scans
Lunar scans are performed using different technologies and methods, each with advantages. Some of the most commonly used methods include:
- Optical Imaging: This is the traditional method of scanning the Moon using high-resolution cameras and telescopes. Optical imaging captures detailed images of the surface, revealing craters, ridges, and other geological features.
- Radar Scans: Radar scans penetrate the surface of the Moon to gather information about its composition and structure beneath the visible surface. This method is particularly useful for studying the Moon’s polar regions, where ice deposits may be present.
- Infrared Scanning: Infrared sensors detect heat patterns on the Moon’s surface. This helps scientists identify mineral deposits, as different materials emit different heat levels.
- LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LIDAR technology uses laser beams to create highly accurate topographic maps of the Moon’s surface. This helps scientists measure the elevation of lunar features and identify potential hazards for future missions.
How Lunar Scans Help Us Understand the Moon
Lunar scans provide critical information about the Moon’s surface and history. By analyzing these scans, scientists can piece together the Moon’s geological past, including how it was formed and evolved over billions of years.
1. Surface Composition
One of the most important information obtained from lunar scans is the composition of the Moon’s surface. By analyzing the minerals and elements present, scientists can determine the types of rocks and soils found on the Moon. These scans have revealed that the Moon’s surface mainly comprises silicate minerals, such as basalt and anorthosite, and traces of other elements like titanium, iron, and magnesium.
2. Impact Craters and Geological Features
Lunar scans have provided a detailed map of the Moon’s surface, revealing various geological features. One of the most prominent features of the Moon is its vast number of impact craters, which were created by asteroids and comets colliding with the Moon’s surface over billions of years. Lunar allow scientists to study the size, shape, and distribution of these craters, which in turn helps us understand the history of cosmic impacts on the Moon and other celestial bodies.
3. Water Ice and Resources
One of the most exciting discoveries of lunar scans is detecting water ice at the Moon’s poles. Using radar and infrared scan, scientists have found significant frozen water deposits in permanently shadowed craters at the lunar poles. This discovery has major implications for future lunar exploration, as water is a critical resource for human habitation and can also be used to produce oxygen and fuel.
In addition to water ice, lunar have identified other valuable resources on the Moon, such as helium-3, a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion, and rare earth elements that could be used in advanced technologies.
4. Potential for Human Habitation
Lunar scans are crucial for planning future human missions to the Moon. By studying the surface, scientists can identify safe landing sites, areas rich in resources, and potential hazards, such as deep craters or unstable terrain. Additionally, lunar help researchers determine the best locations for establishing lunar bases, considering factors like access to water, sunlight, and natural protection from radiation.
Major Discoveries Through Lunar Scans
Over the past few decades, lunar scans have led to several groundbreaking discoveries. Some of the most notable include:
1. Water Ice at the Moon’s Poles
As mentioned earlier, one of the most significant discoveries made through lunar scans is the presence of water ice at the Moon’s poles. This finding, made by missions like NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), can potentially revolutionize future lunar exploration. Water ice could be used for drinking and producing oxygen and hydrogen for rocket fuel.
2. Lunar Lava Tubes
Another important discovery is the identification of ancient lava tubes on the Moon. These tubes, formed by volcanic activity billions of years ago, could provide a natural shelter for future lunar explorers. They offer protection from radiation, micrometeorites, and temperature extremes, making them ideal locations for establishing lunar habitats.
3. New Insights into Lunar Geology
Lunar scans have provided scientists a deeper understanding of the Moon’s geological history. For instance, lunar have revealed that the Moon’s crust is not uniform; instead, it contains regions with varying thickness and composition. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the Moon’s formation and the processes that shaped its surface over time.
4. Unexpected Volcanic Activity
Through detailed scans of the Moon’s surface, scientists have found evidence of volcanic activity in the past few hundred million years. This discovery challenges previous assumptions about the Moon’s geological activity and suggests it may not be as geologically inactive as previously believed.
The Future of Lunar Exploration
As space agencies like NASA, ESA, and China’s CNSA continue to develop ambitious plans for lunar exploration, the role of lunar scans will only become more critical. Here are some key areas where lunar will continue to shape our understanding of the Moon:
1. Artemis Program and Human Missions
NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon by the late 2020s. Lunar scans will be essential for identifying landing sites, assessing the Moon’s environment, and planning infrastructure for human missions. These scans will also help monitor the health and safety of astronauts as they explore the lunar surface.
2. Lunar Resource Mining
As the demand for resources like rare earth elements and helium-3 grows, lunar resource mining may become a reality. Lunar scans will be instrumental in locating and extracting these resources, which could fuel advancements in technology and energy production.
3. Establishing Lunar Bases
In the future, lunar scans will guide the construction of lunar bases and support sustainable human habitation on the Moon. These scans will help identify the best locations for building habitats, power stations, and other necessary infrastructure.

Conclusion
Lunar scans have provided incredible knowledge about the Moon’s surface and its potential for future exploration. From mapping the Moon’s geological features to detecting water ice and resources, these scans are paving the way for a new era of lunar exploration. As technology advances and we gather more data, we can expect even more exciting discoveries to shape humanity’s understanding of the Moon and our ability to live and work on its surface.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of lunar scans?
Lunar scans help scientists gather data about the Moon’s surface, composition, and geological history. They are essential for planning future lunar missions, locating resources, and understanding the Moon’s environment.
2. What technology is used in lunar scans?
Lunar scans use various technologies, including optical imaging, radar scans, infrared sensors, and LIDAR. These tools provide detailed images and data about the Moon’s surface and subsurface.
3. What has been the most significant discovery from lunar scans?
The discovery of water ice at the Moon’s poles has been one of the most significant breakthroughs. This finding carries major implications for future lunar exploration. Water is vital for human survival and could fuel rockets.
4. How will lunar scans help in establishing lunar bases?
Lunar scans will identify safe locations for lunar bases, assess resource availability, and protect future habitats from hazards like radiation and extreme temperatures.
5. Are lunar scans only done by NASA?
Multiple space agencies, including NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and China’s National Space Administration (CNSA), conduct lunar scans.These agencies collaborate and share data to advance our understanding of the Moon.
Explore more: hadokin